Abstract
Introduction
Several recent pivotal trials have changed the standard of care for patients with limited stage (LS) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) to minimize the number of chemoimmunotherapy cycles and/or eliminate the need for radiotherapy (RT) without compromising excellent long-term outcomes (Poeschel 2019; Persky 2020; Bologna 2021). However, there may be subsets of patients where an abbreviated treatment approach is insufficient. With this in mind, Bobillo (2021), retrospectively reviewed pts with LS DLBCL treated with RCHOP (4-6 cycles) +/- RT and reported an extranodal (EN) presentation had shorter PFS and OS compared with nodal presentation. In these pts, consolidative RT prolonged survival in pts with EN disease, especially those with a positive PET scan at the end of chemotherapy. We sought to validate these findings by analyzing patients with LS DLBCL treated on 3 consecutive SWOG studies (S0014, S0313, S1001).
Methods
From 4/1/00 - 6/1/16, 234 eligible patients with non-bulky (exception of 2 patients on S0014) LS DLBCL were accrued to S0014 (n=60), S0313 (n=43), or S1001 (n=131), Enrolled pts received therapy with RCHOP x 3 + involved field radiotherapy (IFRT; 26%); RCHOP x 3 + IFRT + ibritumomab tiuxetan (24%); or RCHOP x 4 (51%). In S1001, an interim PET (iPET) scan was performed after RCHOP x 3 and considered negative if the Deauville Score was ≤3. Fisher's exact test compared the distribution of the characteristics and treatments received at 2-sided a of .05. PFS was calculated from date of randomization until progression/relapse/death. OS was calculated from date of randomization until death. PFS and OS estimates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
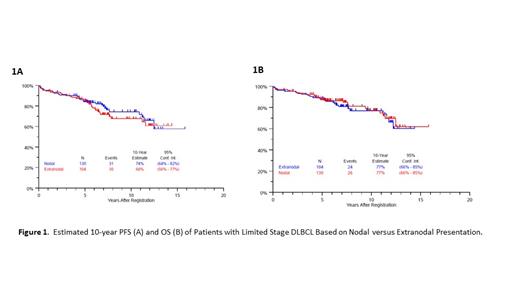
Median follow-up is 7 years (range 1.1 - 15.8 years). Median age was 62 (range 18 - 85) and 68% had stage-modified international prognostic index (sm-IPI) of 0-1. Of the 234 pts, 104 (44%) had EN disease. Most common sites of EN disease were head & neck (n=55; nasopharynx=14; oral cavity=17; orbit=2; parotid=4; sinus=7; submandibular gland=1; thyroid=9; vocal cord=1), skin/soft tissue/muscle (n=12), gastrointestinal tract (n=11), bone (n=6), and breast (n=6). Clinical characteristics (age, stage, LDH, sm-IPI) and treatments received between EN and nodal disease groups were not statistically different. For the whole group, estimated 10-year PFS and OS were 71% (95% CI: 64% - 77%) and 77% (95% CI: 69% - 83%), respectively. For patients with extranodal versus nodal disease, there was no difference in the estimated 10-year PFS (74% vs 68%; 2-sided logrank p-value=.51, Figure 1A) or 10-year OS (77% vs 77%; 2-sided logrank p-value=.65; Figure 1B). For the 55 pts with EN disease of the head & neck, estimated 10-year PFS and OS were 61% (44% - 74%) and 77% (63% - 87%). Among the 104 pts with EN disease who received versus did not receive IFRT, there was no difference in the estimated 5-year PFS (83% vs 87%; 2-sided logrank p-value=.52) or 5-year OS (85% vs 92%; 2-sided logrank p-value=.28). Of 55 pts with EN disease treated on S1001, 5 (9%) pts had iPET+, 47 (85.5%) pts had iPET-, and 3 (5.5%) pts did not have iPET. In the 5 pts with EN disease and iPET+, all received IFRT and 1 progressed. There were 50 pt deaths. Of these, cause of death was lymphoma in 16 (32%), second cancer in 6 (12%), other in 15 (30%), and unknown in 13 (26%).
Conclusions
Patients with LS DLBCL treated on 3 SWOG studies had excellent and prolonged PFS and OS regardless of EN versus nodal presentation, or whether they received consolidative IFRT or not. Our dataset does not support EN disease as an adverse prognostic factor for pts with LS DLBCL. As such, we do not recommend consolidation with radiotherapy in pts with non-bulky LS DLBCL presenting with EN disease. There were too few patients with EN disease treated on S1001 that had iPET+ to make a recommendation for PET-adapted IFRT. The majority of pts in our dataset had EN disease of the head & neck, which appears to have similar survival as nodal presentation. As seen in previous studies, there was a continuous rate of relapse without plateau of the PFS curves. Most common known cause of death in was lymphoma, which supports the need for long term follow-up.
Stephens: Celgene: Consultancy; Mingsight: Research Funding; Arqule: Research Funding; Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; JUNO: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; Epizyme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Innate Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Leonard: ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS/Celgene, Epizyme, Inc., Genmab, Gilead/Kite, Karyopharm, BMS/Celgene, Regeneron, MEI Pharma, Miltenyi, Roche/Genentech, Sutro: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy. Kahl: Abbvie, ADCT, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Celgene, Teva, Janssen, MTEM, Bayer, InCyte, Adaptive, Genentech, Roche, MEI, KITE, TG Therapeutics, Epizyme, Takeda: Consultancy; Abbvie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Acerta: Research Funding; Research to Practice: Speakers Bureau. Smith: Celgene, Genetech, AbbVie: Consultancy; Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease: Other: Study investigator. Friedberg: Bayer: Other: DSMC ; Novartis: Other: DSMC ; Acerta: Other: DSMC .
ibritumomab tiuxetan is not FDA approved for marketing in DLBCL

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal